Introduction
The National Programme for the Health Care for the Elderly (NPHCE) is an articulation of the International and national commitments of the Government as envisaged under the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), National Policy on Older Persons (NPOP) adopted by the Government of India in 1999 & Section 20 of “The Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007” dealing with provisions for medical care of Senior Citizen.
The Vision of the NPHCE is:
- To provide accessible, affordable, and high-quality long-term, comprehensive and dedicated care services to an Ageing population
- Creating a new “architecture” for Ageing
- To build a framework to create an enabling environment for “a Society for all Ages”
- To promote the concept of Active and Healthy Ageing.
Scope of services
In the programme, it is envisaged providing promotional, preventive, curative and rehabilitative services in an integrated manner for the Elderly in various Government health facilities. The package of services would depend on the level of health facility and may vary from facility to facility. The range of services will include health promotion, preventive services, diagnosis and management of geriatric medical problems (out and in-patient), day care services, rehabilitative services and home based care as needed. Districts will be linked to Regional Geriatric Centres for providing tertiary level care. The services under the programme would be integrated below district level and will be integral part of existing primary health care delivery system and vertical at district and above as more specialized health care are needed for the elderly
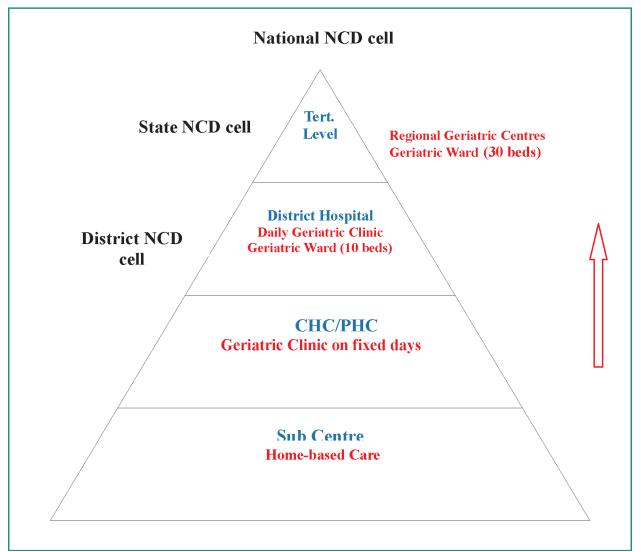
Components of the Program:
- National Health Mission (NHM) Component: Primary & Secondary care service delivery through District Hospitals (DH), Community Health Centres (CHC), Primary Health Centres (PHC), Sub-Centre/Health & Wellness Centres.
- Tertiary Component: Renamed as ‘RashtriyaVaristh Jan Swasthya Yojana’ in 2016-17. These services are being provided though Regional Geriatric Centres (RGCs) located at 19 Medical colleges in 18 states of India and two National Centres of Aging (NCAs) one in AIIMS, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi and another in Madras Medical College, Chennai.
- Research: A Longitudinal Ageing Study in India (LASI) project:-The LASI is a nationally representative survey of older persons in India is being undertaken through International Institute of Population Sciences (IIPS), Mumbai. LASI wave-1 survey (2017-18) covers all 30 states and 6 Union Territories of India with a panel sample size of 72,250 older adults aged 45 years including 31464 people above 60 years of age and above and their spouses regardless of age. LASI collects data on four major subject domains:
- Health: Disease Burden & Risk Factors (Reported and Measured)
- Health Care and Health Care Financing
- Social: Family, Social Network and Social Welfare Programmes for the Elderly
- Economic: Income, Wealth, Expenditure, Employment, Retirement and Pension
The first wave of LASI has been completed and the final report of LASI wave-I released by Hon’ble Union Health Minister on 6th January 2021.
- Community based primary health care approach including domiciliary visits by trained health care workers.
- Dedicated services at PHC/CHC level including provision of machinery, equipment, training, additional human resources (CHC), IEC, etc.
- Dedicated facilities at District Hospital with 10 bedded wards, additional human resources, machinery & equipment, consumables & drugs, training and IEC.
- Strengthening of Regional Geriatric Centers to provide dedicated tertiary level medical facilities for the Elderly, introducing PG courses in Geriatric Medicine, and in-service training of health personnel at all levels.
Program Strategies:
- NPHCE Operational Guidelines








